The Evolution of IASTM: History and Innovations
Introduction to IASTM
If you’ve ever heard about IASTM tools, you might have a vague idea that they’re used on soft tissues. But what exactly are these tools, and why are they so important in physical therapy? Let’s start from the basics.
What are Soft Tissues?
Soft tissues in our bodies include:
- Skin
- Fascia
- Ligaments
- Tendons
- Capsules
- Muscles
Injuries to these tissues can arise from various causes such as direct trauma, repetitive overuse, poor posture, muscle imbalances, and surgeries. Surgeries, while treating the primary condition, often lead to dysfunctions in the surrounding soft tissues due to the cutting of skin and fascia, resulting in scarring. These issues contribute to pain, guarding, and loss of function. Regardless of the injury mechanism, soft tissues are affected and need time and proper intervention to heal.
History of IASTM
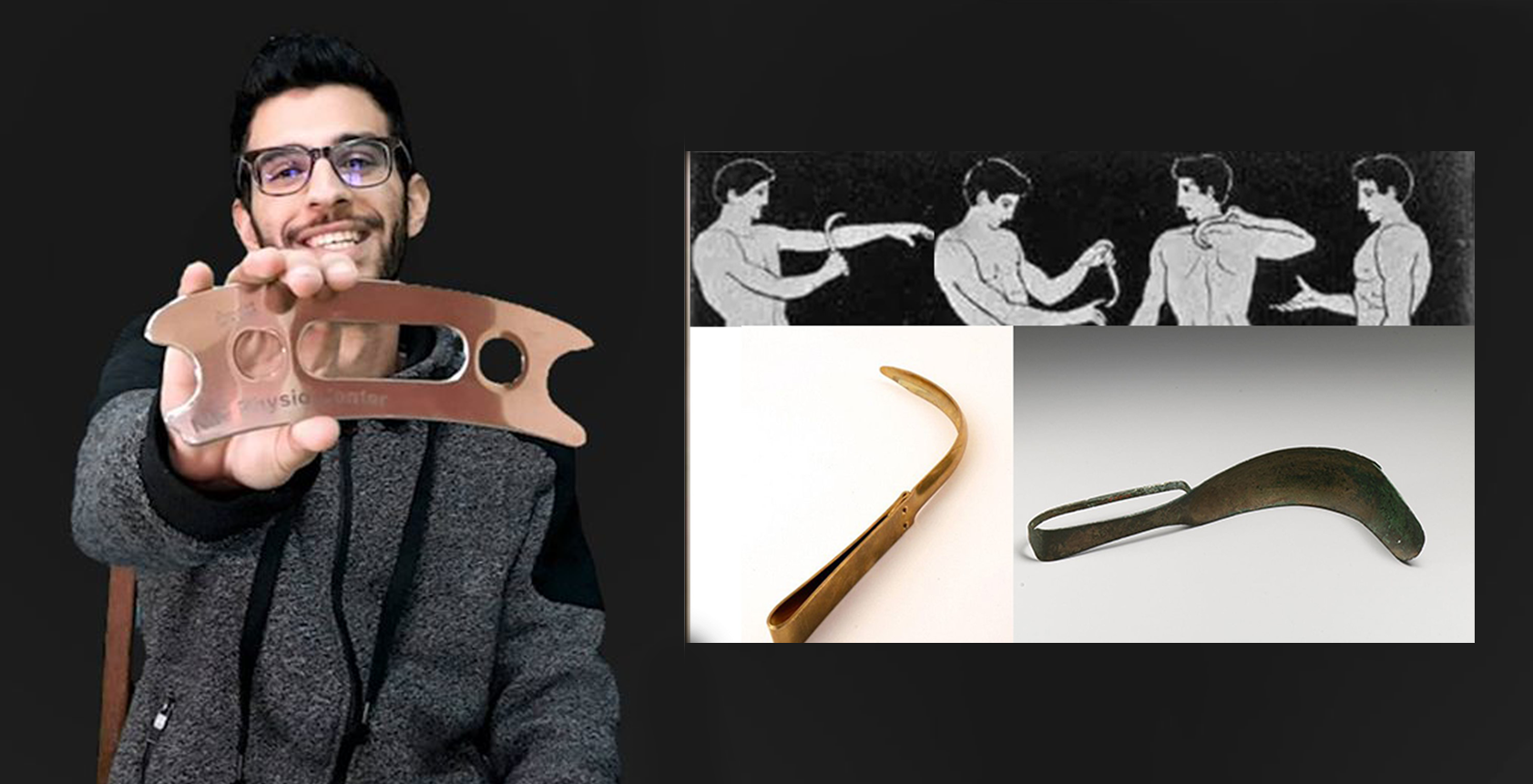
The Origins: Strigils in Ancient Rome
The history of Instrument Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization (IASTM) dates back to ancient Rome, around 220 B.C. The Romans used metal tools called “strigils” to clean their bodies of oils and dirt. While this practice was more about hygiene, it laid the foundation for the concept of using tools to manipulate the body’s soft tissues.
Gua Sha: The Ancient Chinese Practice
In traditional Chinese medicine, a technique called “Gua Sha” emerged. This practice involved using smooth-edged tools to scrape the skin, creating red dots known as therapeutic petechiae. Gua Sha means “to scrape” and was believed to release stagnated blood, thus reducing pain and improving circulation. The scraping causes capillaries to bleed, leaking blood into the skin and creating the characteristic red or purple spots. These spots, or petechiae, typically disappear within a few days.

Modern Developments in IASTM
The Influence of Transverse Friction Massage
In the early 1980s, physical therapist Gail Chamberlin and orthopedist James Cyriax highlighted the importance of transverse friction massage. Their work emphasized the role of this technique in increasing fibroblast proliferation and reducing adhesions. This laid the groundwork for modern IASTM practices.
David Graston: Innovator in IASTM
In the late 1980s, Dr. David Graston, recovering from a knee injury and subsequent surgery, recognized the benefits of cross-friction massage. Dissatisfied with his progress, Graston developed prototypes of tools to enhance the effectiveness of this technique. His innovations led to the creation of the Graston Technique and the first IASTM tool, which he patented for 25 years. This innovation opened the door for various companies to design and market their IASTM tools.

The Science Behind IASTM
IASTM involves using rigid devices to deliver directed, targeted forces to specific tissues. The technique aims to break down scar tissue and fascial restrictions. When you apply these tools with a lubricant, it reduces irritation and allows for more effective treatment.
How IASTM Works:
- Increased Circulation: The scraping action increases blood flow to the affected area, promoting healing.
- Fibroblast Proliferation: The mechanical pressure stimulates fibroblasts, cells that play a critical role in wound healing and tissue repair.
- Breaking Down Scar Tissue: The tools help in breaking down scar tissue, which can restrict movement and cause pain.
Innovations in IASTM Tools
Material and Design Evolution
Initially, IASTM tools were made from metal, like the ancient strigils. Today, they come in various materials, including plastic, jade, and stainless steel. The choice of material can depend on the specific treatment needs and patient comfort. For instance, plastic tools are preferred for patients post-surgery or those experiencing significant pain, while stainless steel tools are used for deeper tissue work on specific trigger points.
Tool Shapes and Functions
Different tools have distinct shapes designed for various body parts and techniques. Some common shapes include:
- Concave and Convex Edges: For broad tissue areas and superficial layers.
- Pointed Edges: For targeted, deep tissue work.
- Rounded Edges: For gentle, soothing strokes.

Application Techniques in IASTM
Preparation and Lubrication
Before beginning an IASTM session, applying a lubricant is essential. This prevents irritation and ensures smooth tool movement over the skin. The right amount of lubricant is crucial – too little can cause discomfort, while too much can make the tool slippery and reduce effectiveness.
Techniques and Strokes
- Sweeping: Long, broad strokes to cover large areas.
- Fanning: Curved strokes for specific muscle groups.
- Brushing: Light, rapid strokes to increase circulation.
- Strumming: Cross-fiber strokes to target specific adhesions.
- J-Stroke: Deep tissue strokes for breaking down scar tissue.
Each technique serves a different purpose, from warming up the tissue to breaking down deep adhesions.
IASTM in Modern Physical Therapy

Clinical Benefits
IASTM has been integrated into various physical therapy practices due to its effectiveness in:
- Reducing Pain: By alleviating tissue restrictions and promoting circulation.
- Enhancing Mobility: By breaking down scar tissue and fascial adhesions.
- Speeding Up Recovery: By stimulating the body’s healing processes.
Patient Experiences and Testimonials
Many patients report significant improvements in pain levels and mobility after IASTM sessions. It’s important for therapists to explain the process and set realistic expectations, as some discomfort and redness are normal.
Educational Resources
For those interested in mastering IASTM techniques, consider enrolling in my course, “A1 IASTM Instrument Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization,” available on Udemy. This comprehensive course covers all aspects of IASTM, from basic techniques to advanced applications, helping you enhance your practice and provide better care for your patients.
Enroll in the A1 IASTM Course on Udemy
Conclusion
The evolution of Instrument Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization (IASTM) reflects a rich history of innovation and adaptation. From ancient strigils to modern-day Graston tools, the journey of IASTM is a testament to the continuous quest for effective therapeutic techniques. By understanding its history and innovations, we can appreciate the profound impact IASTM has on physical therapy today.
Unlocking the path to physiotherapy excellence, IASTM stands as a cornerstone of modern manual therapy, providing therapists with powerful tools to enhance patient care and outcomes.